STEP 1
Make a directory inside your “tessel-code” folder called “accelerometer”, change directory into that folder, and initialize a tessel project:
mkdir accelerometer; cd accelerometer; t2 initSTEP 2
Plug the accelerometer module into Tessel port A with the hexagon/icon side down and the electrical components on the top, then plug Tessel into your computer via USB.
STEP 3
Install by typing npm install accel-mma84 into the command line.
npm install accel-mma84STEP 4
Rename “index.js” to “accelerometer.js” and replace the file’s contents with the following:
// Any copyright is dedicated to the Public Domain.
// http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/
/*********************************************
This basic accelerometer example logs a stream
of x, y, and z data from the accelerometer
*********************************************/
var tessel = require('tessel');
var accel = require('accel-mma84').use(tessel.port['A']);
// Initialize the accelerometer.
accel.on('ready', function () {
// Stream accelerometer data
accel.on('data', function (xyz) {
console.log('x:', xyz[0].toFixed(2),
'y:', xyz[1].toFixed(2),
'z:', xyz[2].toFixed(2));
});
});
accel.on('error', function(err){
console.log('Error:', err);
});Save the file.
STEP 5
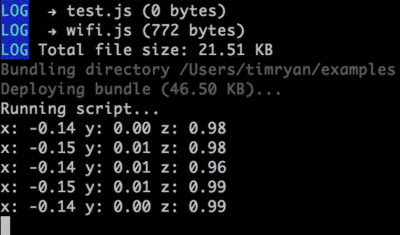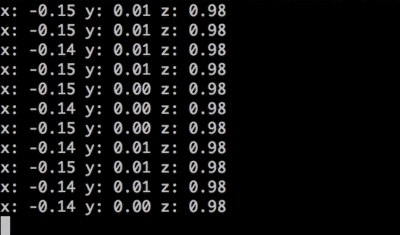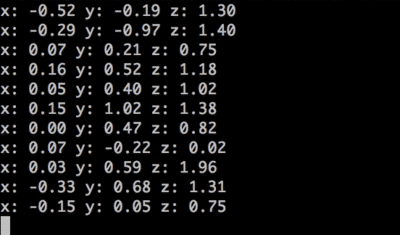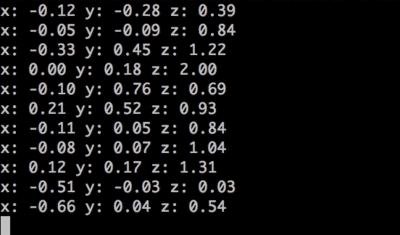
In your command line, t2 run accelerometer.js
Watch x, y, and z values appear in your terminal! Move the Tessel module around to see acceleration along different axes.
Bonus: Instead of just printing data, can you make the accelerometer tell you something useful? Make the Tessel log whether it’s right side up or upside down.
To see what else you can do with the accelerometer module, see the module docs here.
STEP 6
What else can you do with a accelerometer module? Try a community-created project.




